
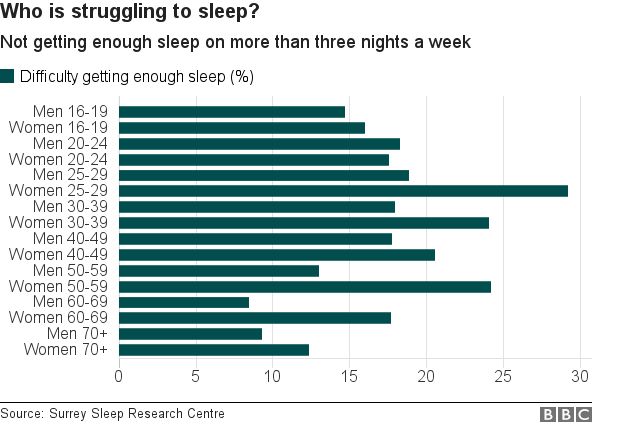
Alpha, beta, theta, gamma, and delta waves are all seen in the different stages of sleep. The amplitude of EEG waves at a particular frequency corresponds to various points in the sleep-wake cycle, such as being asleep, being awake, or falling asleep. The electrical activity seen on an EEG represents brain waves. Sleep researchers also use simplified electrocardiography (EKG) for cardiac activity and actigraphy for motor movements. Simultaneous collection of these measurements is called polysomnography, and can be performed in a specialized sleep laboratory. Key physiological methods for monitoring and measuring changes during sleep include electroencephalography (EEG) of brain waves, electrooculography (EOG) of eye movements, and electromyography (EMG) of skeletal muscle activity. All sleep, even during the day, is associated with the secretion of prolactin. ĭuring slow-wave sleep, humans secrete bursts of growth hormone. In other words, sleeping persons perceive fewer stimuli, but can generally still respond to loud noises and other salient sensory events. In quiet waking, the brain is responsible for 20% of the body's energy use, thus this reduction has a noticeable effect on overall energy consumption. In areas with reduced activity, the brain restores its supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule used for short-term storage and transport of energy. The brain uses significantly less energy during sleep than it does when awake, especially during non-REM sleep. The most pronounced physiological changes in sleep occur in the brain. This disrupts the release of the hormone melatonin needed to regulate the sleep-cycle. Common sources of artificial light include outdoor lighting and the screens of electronic devices such as smartphones and televisions, which emit large amounts of blue light, a form of light typically associated with daytime. The use of artificial light has substantially altered humanity's sleep patterns. Humans may suffer from various sleep disorders, including dyssomnias such as insomnia, hypersomnia, narcolepsy, and sleep apnea parasomnias such as sleepwalking and rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder bruxism and circadian rhythm sleep disorders. Sleep is a highly conserved behavior across animal evolution, likely going back hundreds of millions of years. The diverse purposes and mechanisms of sleep are the subject of substantial ongoing research. The internal circadian clock promotes sleep daily at night.
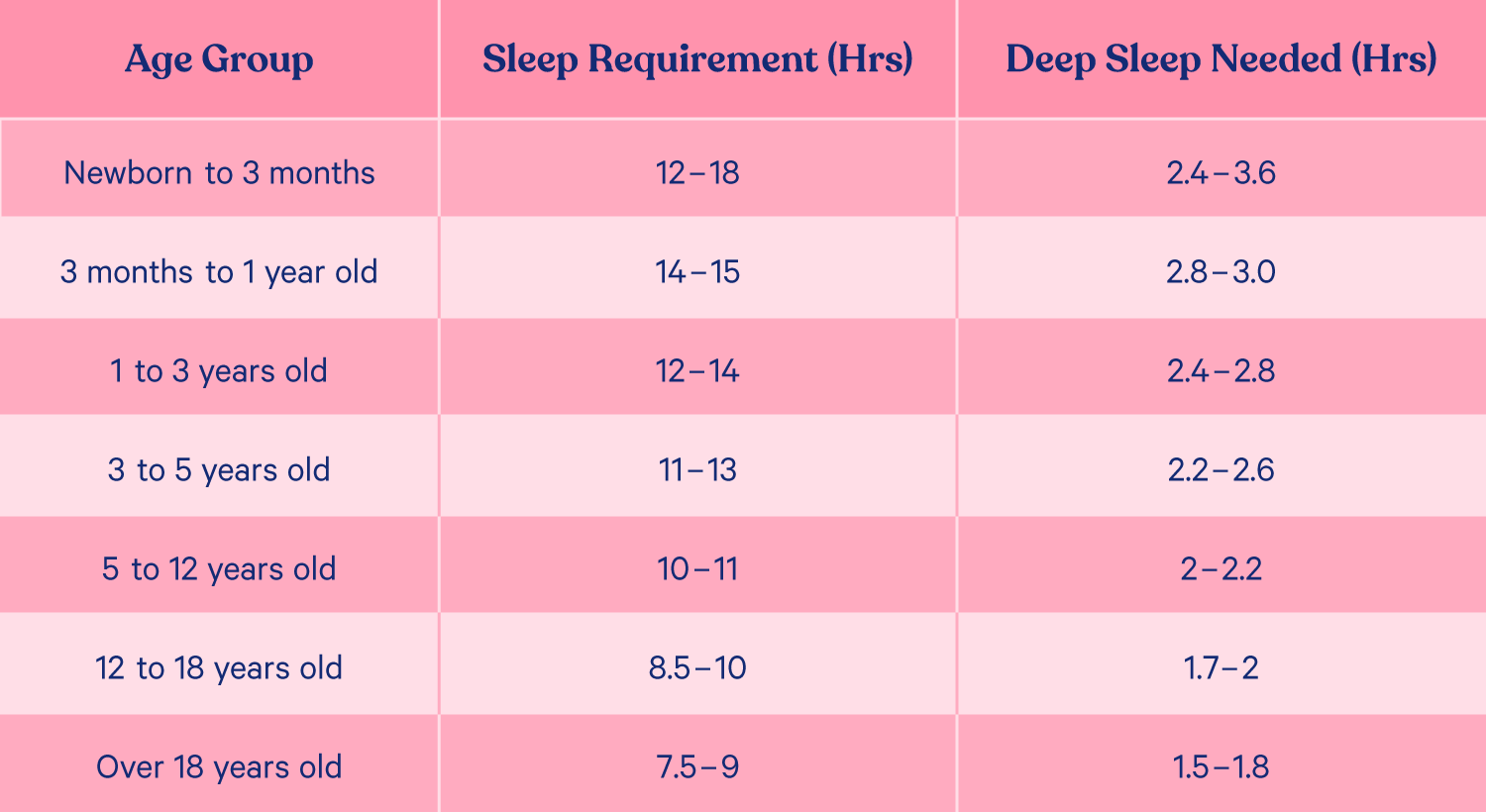
Dreams are a succession of images, ideas, emotions, and sensations that usually occur involuntarily in the mind during certain stages of sleep.ĭuring sleep, most of the body's systems are in an anabolic state, helping to restore the immune, nervous, skeletal, and muscular systems these are vital processes that maintain mood, memory, and cognitive function, and play a large role in the function of the endocrine and immune systems. Although REM stands for "rapid eye movement", this mode of sleep has many other aspects, including virtual paralysis of the body. Sleep occurs in repeating periods, during which the body alternates between two distinct modes: REM and non-REM sleep. While sleep differs from wakefulness in terms of the ability to react to stimuli, it still involves active brain patterns, making it more reactive than a coma or disorders of consciousness. During sleep, there is a decrease in muscle activity, and interactions with the surrounding environment. Sleep is a state of reduced mental and physical activity in which consciousness is altered and sensory activity is inhibited to a certain extent. For other uses, see Asleep (disambiguation) and SLEPT analysis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
